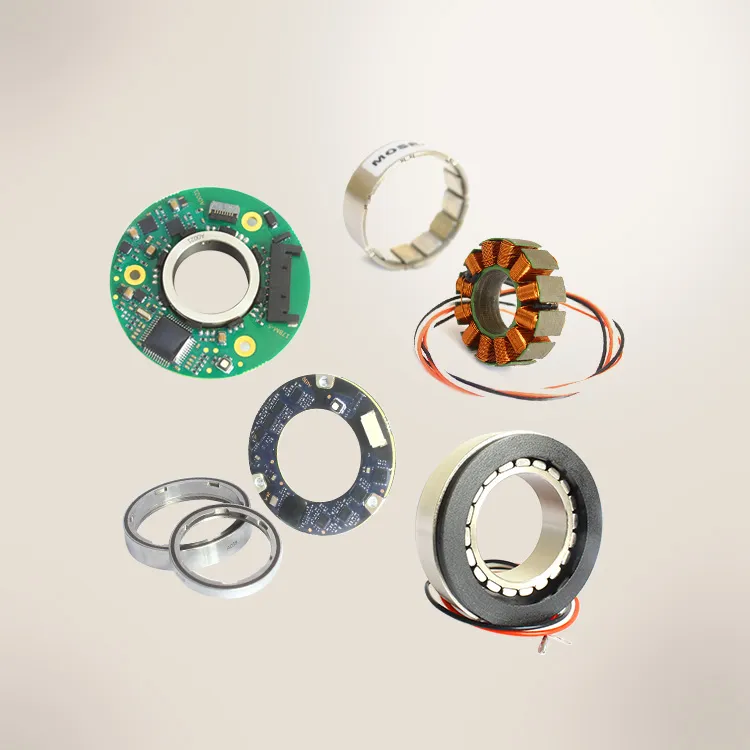
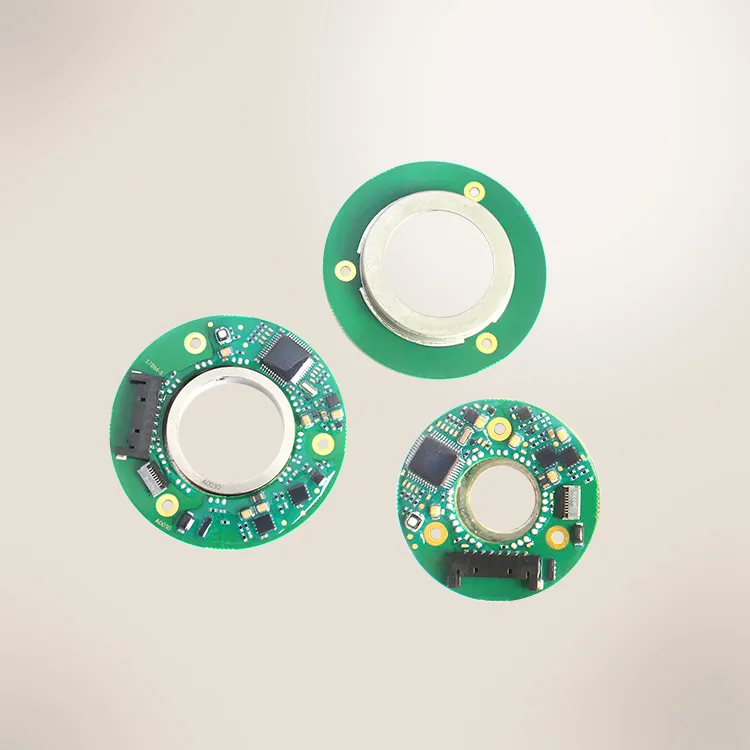
Magnetic Encoders in High‑Performance Automation
1. Introduction
High-performance automation demands precision, reliability, and durability. Yet, many traditional encoders—especially optical ones—struggle in real-world environments filled with dust, oil, vibration, and temperature fluctuations.
The result? Inaccurate feedback, frequent maintenance, and costly downtime.
For industries like robotics, medical devices, direct-drive motors, and industrial automation, even the slightest signal error or encoder failure can disrupt production lines, reduce efficiency, or compromise safety. In competitive global markets, where every second counts, relying on fragile sensing technology is no longer an option.
Mosrac takes this technology further with its advanced S-Series and T-Series innovations, engineered for ultra-thin design, high precision, and seamless integration. Together, they set a new benchmark in modern automation, enabling smarter, more reliable, and future-ready systems!
2. What Are Magnetic Encoders & Why Mosrac?
Magnetic encoders are position-sensing devices that use magnetic fields to determine angular position. Unlike optical encoders, which shine light through patterns on a disk, magnetic encoders rely on a magnet (often a ring or disk magnetized with north-south poles) attached to the rotating shaft.
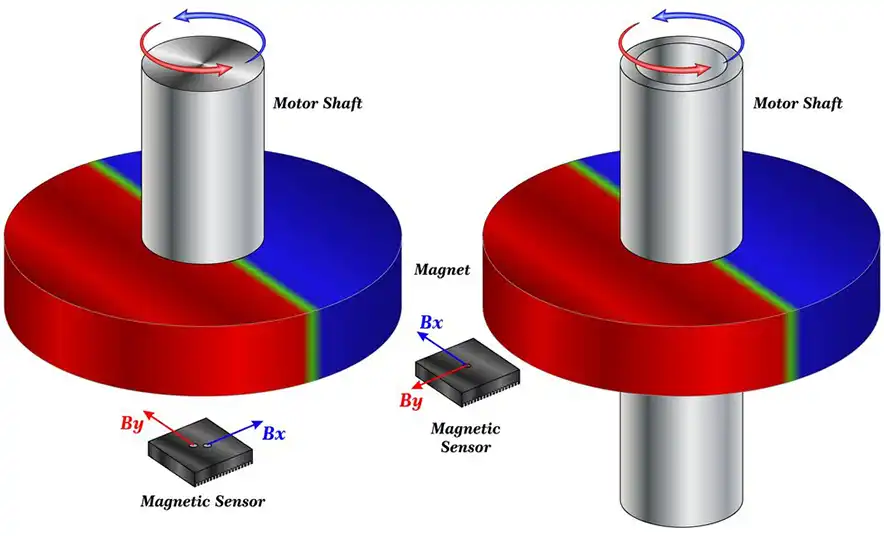
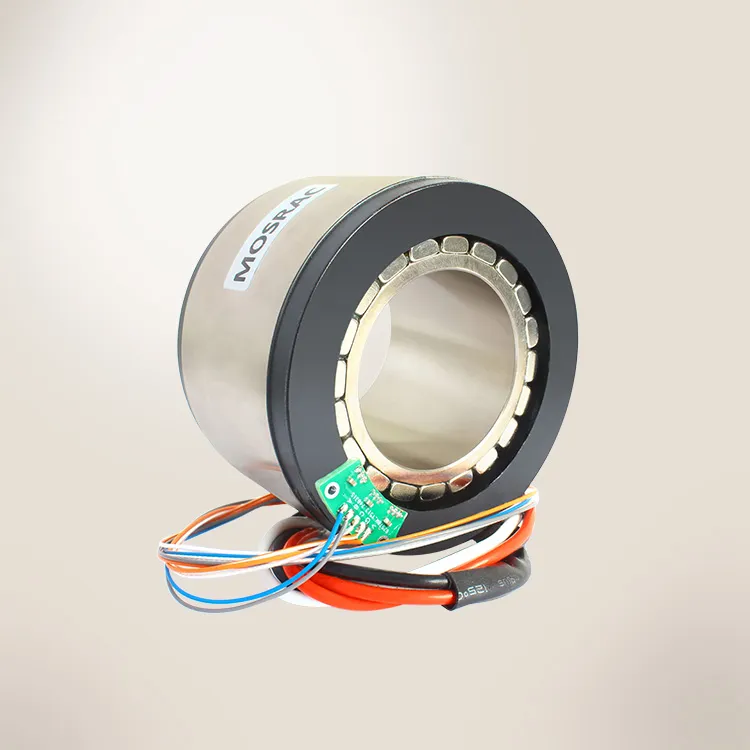
Shaft - End Configuration Magnetic Encoder
Once the shaft turns, Hall-effect sensors or other magneto-resistive sensors on the stator detect changes in the magnetic field. These signals are then converted into digital position data. This sensing method isn’t disrupted by dust or oil, so magnetic encoders can operate reliably in environments that would cripple traditional encoders. They are fully contactless, there’s no physical brush or contact dragging, which means no wear and tear, and minimal maintenance over the device’s lifespan.
Magnetic encoders come in two main types:
◉ Incremental Magnetic Encoder: Produces a series of pulse signals as it rotates, which a controller counts to track movement. However, it only provides relative motion information and typically requires a reference “home” cycle to know the actual position.
◉ Absolute Magnetic Encoder: Outputs a unique digital code or angle value for each shaft position, ensuring the exact angle is known immediately upon power-up, without requiring a homing routine. They can be single-turn (measuring within one revolution) or multi-turn (tracking position over multiple revolutions, often using counters or battery backup).
For high-performance automation, absolute encoders are often preferred because they eliminate uncertainty; the system always knows the exact position, improving safety and control accuracy.
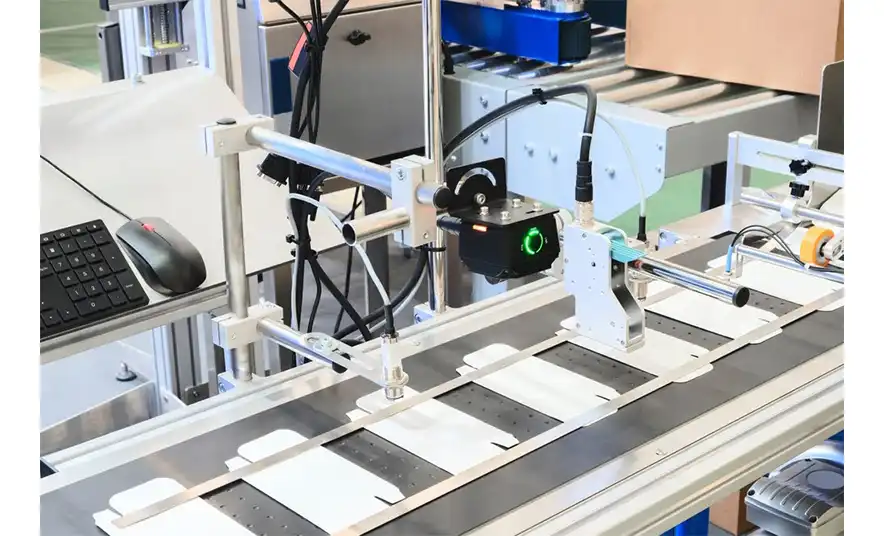

Encoder used in Automatic Packaging Conveyor Line
Mosrac is a leading innovator in the magnetic encoder arena, offering state-of-the-art solutions tailored for modern automation needs. Their product lineup includes:
↪️ S-Series (Magnetic Absolute Encoders)
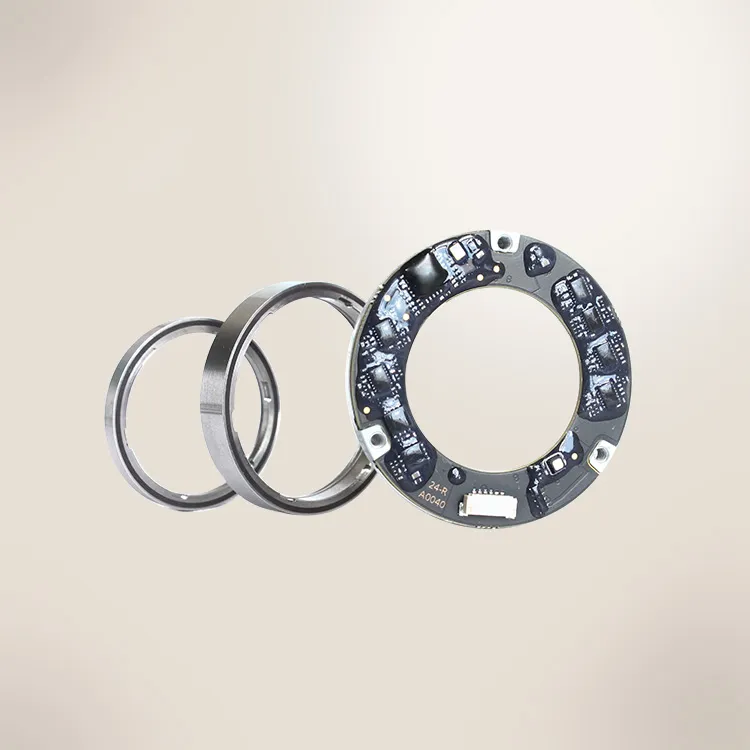
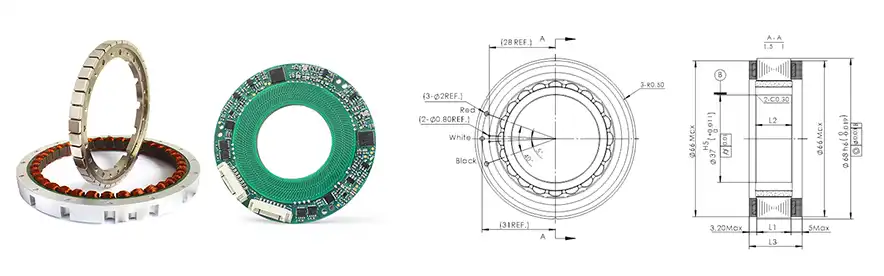
These are ultra-thin, high-precision encoders designed for applications where space is limited but accuracy is paramount. The S-Series provides up to 17-bit single-turn resolution with angular accuracy around ±0.05°. Remarkably, the entire encoder is only about 6–7 mm thick, meaning it can be slipped into tight spaces such as compact servo motors or gearboxes. The S-Series features a hollow shaft design, allowing it to mount around motor shafts or machine axes without adding bulk. Multiple output interface formats are supported – SSI, BiSS-C, RS-485, RS-422, even proprietary protocols like Tamagawa-compatible T-485, and high-speed bus or periodic interfaces, ensuring easy integration into diverse control systems.
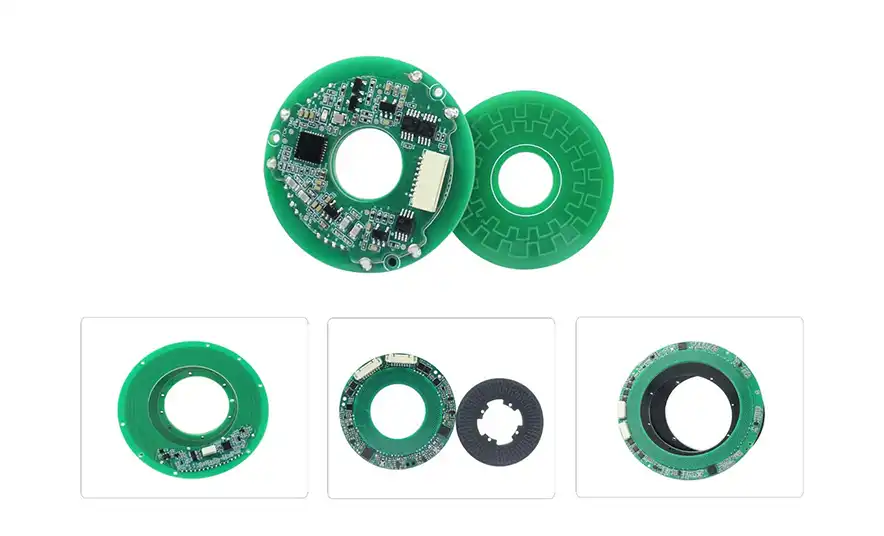

17-bit & 24-Bit High-Resolution Magnetic Absolute Rotary Encoder - Mosrac
The engineering gives these encoders strong immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electrical noise, so they maintain stable readings even near motors or drives. In short, the S-Series magnetic encoders deliver optical-grade resolution in a slim, ultra‑thin absolute encoder package that is rugged and EMI-shielded for industrial environments.
↪️ T-Series (Magnetic Dual Encoders)
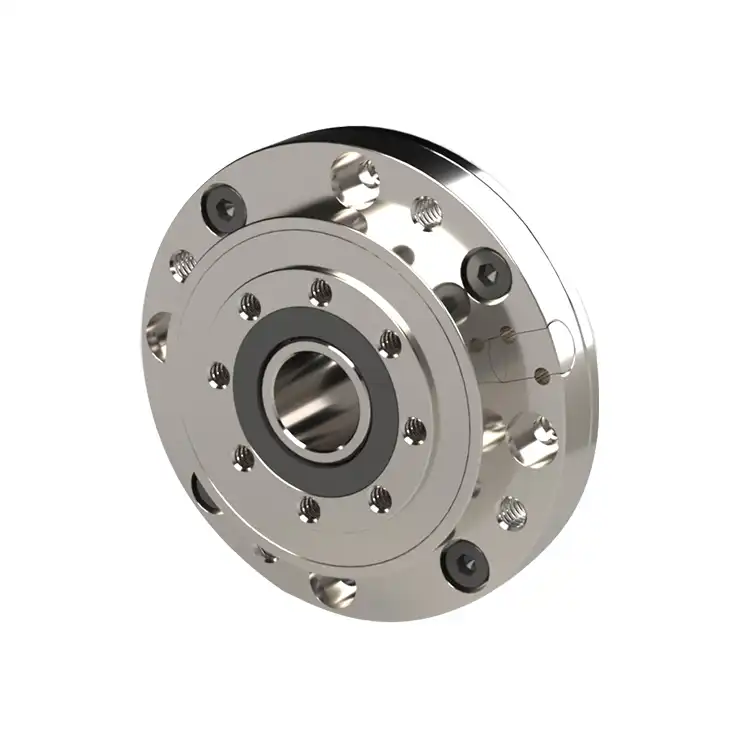
The T-Series takes magnetic encoding a step further by measuring two rotational axes simultaneously in one compact unit. Designed specifically for robot-integrated joints, a T-Series encoder actually contains two encoders in one: an inner and an outer encoder, each providing up to 24-bit resolution and an extraordinary accuracy of approximately ±0.01°. This dual-axis magnetic encoder can thus provide feedback for both a motor’s rotor and a joint’s output shaft simultaneously (or any two coaxial shafts), which is ideal for advanced robotic arms or cobots that have limited space for sensors.
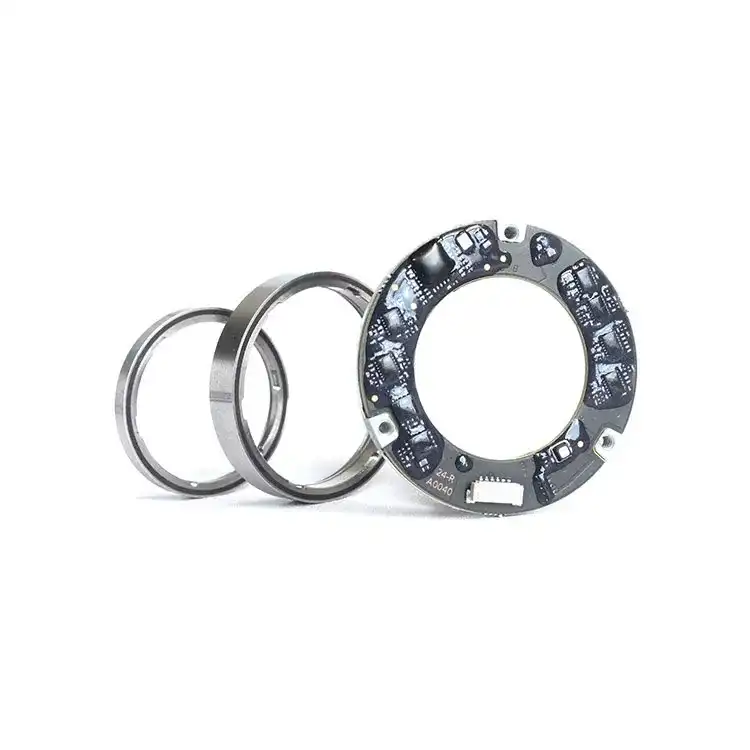

T-Series Magnetic Dual Encoder - Mosrac
Despite this complexity, the T-Series remains extremely compact – Mosrac cites it as the “world’s most compact” dual encoder, with a radial thickness of only ~7 mm on each side. The T-Series outputs absolute position data over robust interfaces like RS-485 or BiSS-C, and is built with high resistance to environmental disturbances. It achieves “photoelectric-like” performance in resolution and accuracy, yet it’s far more robust against shock, vibration, or contaminants.
These dual encoders are custom-made for robotic joints, where integrating two sensors separately would be difficult – the T-Series simplifies design by combining them. Additionally, they feature rapid boot-up (position available in ~15 ms after power-on) and high ESD (electrostatic discharge) tolerance, reflecting a high level of attention to real-world operating conditions.
3. Technical Principles & Mosrac Engineering
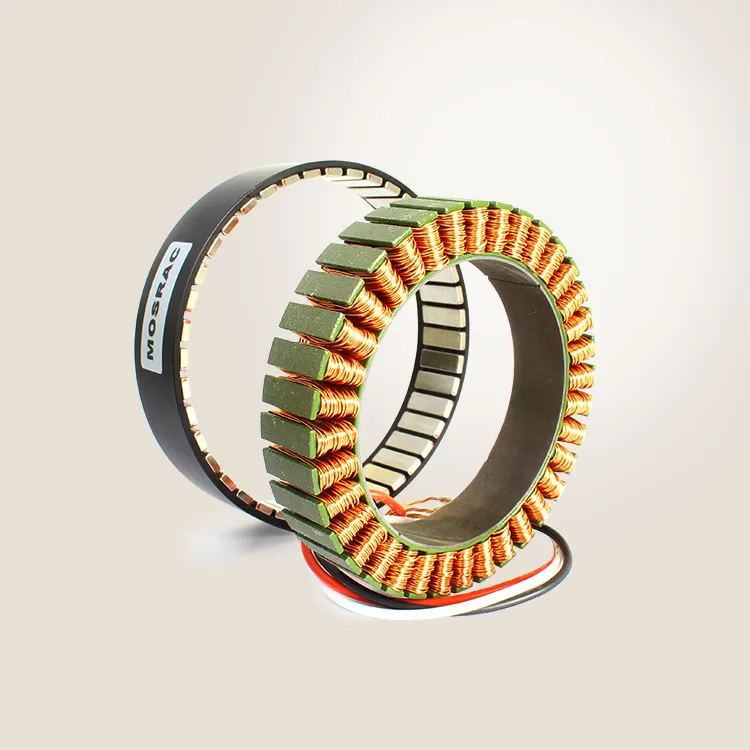
A magnetic encoder is a magnetic ring (rotor) paired with an array of Hall-effect sensors on the stator. The magnetic ring is precisely magnetized with alternating north and south poles. Once it rotates, the sensors measure the changing magnetic flux and produce signals corresponding to the angular position.
The encoders use multiple high-precision Hall sensors in a coordinated way, along with a custom conditioning circuit, to interpolate these signals into a very fine position reading. The raw data is then processed with precision calibration algorithms.
↪️Factory Calibration
During manufacturing, Mosrac calibrates each S-Series and T-Series unit against known references and stores unique magnetic field correction data in the device. This calibration compensates for any tiny variances in the magnetic ring or sensor alignment, yielding optimal measurement accuracy out of the box. It also means the output of encoder is linearized and ready to use without user calibration – installation is simplified, and high accuracy is maintained over the device’s life.
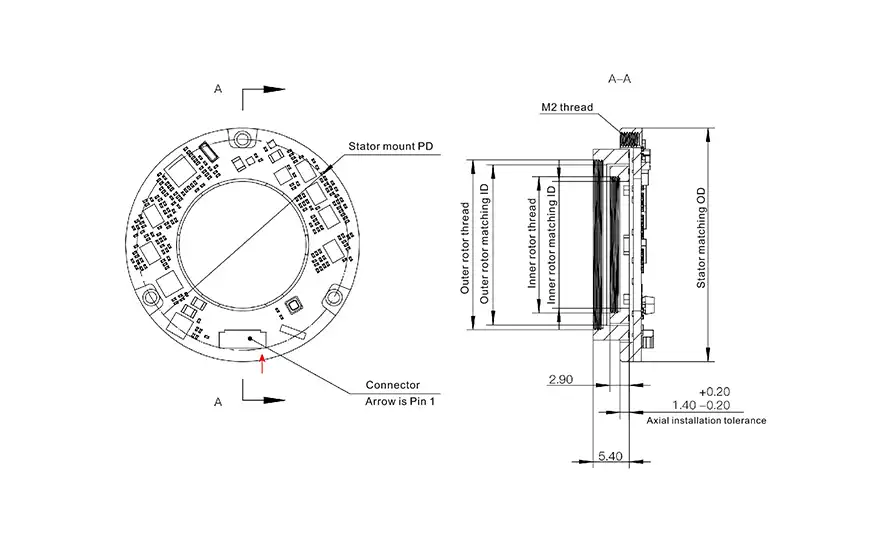
Drawing for T-Series Magnetic Dual Encoder
By shipping each encoder with this factory-set calibration, Mosrac ensures that when you integrate it into your system, you get precise results immediately and consistently.
↪️Interference Shielding Technology
Magnetic sensors can be susceptible to stray electromagnetic fields (from nearby motors, drives, or cables). Mosrac addresses this by incorporating shielding materials and clever circuit design to block external magnetic noise. Resultantly, these encoders can operate with high precision even in environments with substantial electromagnetic interference (EMI) – a common scenario in factories with many electric motors. This shielding, combined with the inherently sealed construction of magnetic encoders, allows them to function normally in conditions that would disturb other sensors.
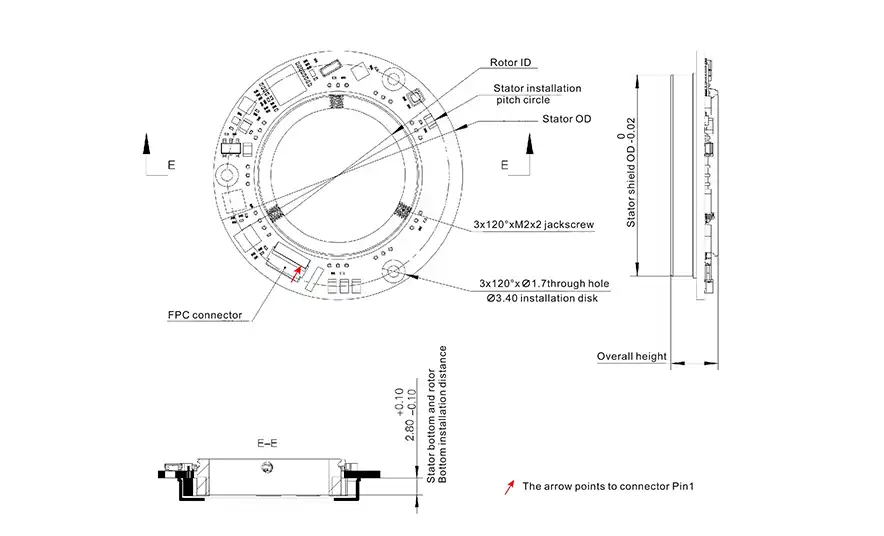
Drawing for S-Series Magnetic Encoder
Mechanically, Mosrac encoders use a hollow, separated rotor-stator structure, which doesn’t impose bearing loads or tight coupling demands. The rotor (magnetic ring) can be mounted on the rotating shaft, and the stator attached to the housing;
Mosrac’s design provides a “tolerance fit” that is easy to assemble while keeping an optimal sensor gap. The hollow shaft design means you can pass cables or other components through the encoder center, and it can be mounted at virtually any point in a drivetrain (at the motor shaft, at a gearbox output, etc.) without changing the layout.
There is no need for a clear optical path or delicate alignment like with optical encoders – the magnetic field permeates even if the environment has some dust or if the mounting isn’t perfectly concentric (within reasonable tolerances). This means plug-and-play precision, even in applications where setup space is tight or conditions are less than ideal.
↪️Mosrac S-Series: Ultra-Thin Absolute Encoders
✔Hollow Structure: For easy shaft integration and space efficiency
✔Multiple Interface Options: SSI, BiSS-C, RS485, RS422, Tamagawa-compatible T485, BUS, PERIOD
✔Operating Speed: Stable at >20,000 rpm for high-speed automation systems
✔Resolution & Accuracy: Up to 17-bit with ±0.05° accuracy
✔High EMI Resistance: Ensuring reliability in industrial and medical devices
✔Designed For: Servo Motors, Direct-Drive Torque Motors, and Compact Automation Machinery
↪️Mosrac T-Series: Magnetic Dual Encoders
✔Compact Dual-Axis Design: Enabling two-axis position feedback in a single module
✔Output Interfaces: RS-485 and BiSS-C for seamless digital integration
✔Ultra-High Resolution: 24-bit with ±0.01° accuracy
✔High ESD Tolerance: Safeguarding against electrostatic discharge in sensitive applications
✔Multi-Temperature Range Options: Ensuring stable performance across diverse operating conditions
✔Ideal For: Robotic Joints, Collaborative Robots (cobots), and Aerospace Grade Automation
By combining advanced shielding, calibration, and compact design, Mosrac has created a new standard in encoder engineering—balancing precision, durability, and easy integration to empower the next generation of high-performance automation.
4. Key Features to Look for in a Magnetic Encoder
When choosing a rotary encoder for a demanding application, there are several critical features and performance factors to consider. The magnetic encoders excel in many of these areas.
Let’s break down the key features into categories:
1️⃣Durability & Environmental Resilience
Magnetic encoders excel in harsh conditions because they rely on magnetic fields rather than fragile optics. Dust, oil, or moisture won’t disrupt operation, unlike optical encoders.
Mosrac enhances durability with a sealed, contactless design and no moving parts that could wear out. Their encoders resist vibration, shock, and electrical noise with EMI shielding, and operate across a wide temperature range (up to 125 °C).
The nano-thin, hollow structure allows installation in tight or protected spaces. This resilience ensures long-lasting reliability, reducing downtime from failures in harsh industrial environments.
2️⃣Compactness & High Precision
Automation systems often demand accuracy in tight spaces. S-Series by Mosrac delivers 17-bit resolution and ±0.05° accuracy in a compact 6–7 mm design, making it ideal for motor housings or gearboxes.
For higher precision, the T-Series offers 24-bit dual-axis resolution and ±0.01° accuracy in a compact form factor, ideally suited for robotic joints and medical devices. Both series maintain accuracy through factory calibration, compensating for environmental changes.
This balance of miniature size and high precision ensures smooth motion control and design flexibility in space-constrained, high-performance automation systems.
3️⃣Reliability & Low Maintenance
The magnetic encoders are contactless and sealed, eliminating wear points common in optical encoders. This design provides long MTBF (mean time between failures) with little to no maintenance. Their absolute architecture removes the need for homing sequences, allowing systems to resume instantly after power cycles.
The T-Series starts up in just ~15 ms, delivering stable feedback without delays. Supported by robust interfaces such as SSI and BiSS-C, encoders maintain consistent accuracy over the years of use. The result: fewer shutdowns, reduced service costs, and dependable performance in demanding automation environments.
4️⃣Ease of Integration & Flexibility
Engineers value components that simplify design. Mosrac encoders feature a hollow, modular structure for easy mechanical fit and tolerance to slight misalignments. They offer broad interface support (SSI, RS-485, BiSS-C, RS-422, Tamagawa-compatible T485, etc.), making integration straightforward with existing controllers.
The low-profile form factor allows installation inside motors, direct-drive axes, or robot joints without redesign. Options like multi-turn absolute counting further expand usability. Combined with Mosrac’s technical support and documentation, these encoders offer plug-and-play flexibility, reducing complexity in both new system designs and retrofits.
5️⃣Cost Effectiveness
Long-term savings make Mosrac encoders highly cost-effective. Their durability reduces replacement cycles, and minimal maintenance lowers labor costs. Unlike optical encoders, they don’t require filtered enclosures or strict environmental controls, cutting auxiliary system expenses. EMI shielding and wide temperature tolerance prevent costly failures, protecting other equipment from damage caused by feedback errors.
With premium performance at competitive pricing, Mosrac encoders deliver high accuracy without overspending. Their extended lifespan further reduces the total cost of ownership, ensuring manufacturers achieve a strong ROI while avoiding downtime or frequent part replacements.
6️⃣Lifecycle Value
Beyond immediate specs, lifecycle value ensures an encoder performs reliably for years. Mosrac’s encoders use solid-state sensors with no wear points, enabling millions of rotations without degradation.
Factory calibration and robust materials minimize drift, maintaining accuracy over prolonged use. They withstand shock, vibration, and temperature swings without compromising performance, ensuring consistent feedback in high-demand applications.
This longevity reduces mid-life retrofits, extends motor and system lifespans, and improves overall automation efficiency. With reliable operation, minimal upkeep, and sustained accuracy, Mosrac encoders guarantee long-term ROI for industrial automation investments.
In essence, the lifecycle value of magnetic encoders is seen in their sustained reliability, minimal upkeep, and the extended longevity they confer to automation systems.
Over years of high-demand use, they maintain consistent performance, which means your machines maintain consistent output and efficiency. This makes encoders a strategic choice for any company looking to optimize not just immediate performance, but also long-term operational return on investment.
5. Mosrac Products & Use Cases in High-Performance Automation
Having explored the features in theory, let’s examine how magnetic encoders are applied in real-world automation and how to select the right model for your needs.
Product Highlights
S-Series Magnetic Encoders
The S-Series are ultra-thin absolute encoders (single-turn or multi-turn) that combine compact form with high accuracy. At only 6–7 mm thickness, they offer 17-bit resolution, ±0.05° accuracy, and strong EMI immunity.
Their hollow shaft design allows direct integration into motor housings, gearboxes, or robotic grippers without redesign. Available in multiple bore sizes, the S-Series fits confined machinery where precision feedback is critical—such as CNC rotary tables, servo motors, or robotic end effectors.
T-Series Magnetic Dual Encoders
The T-Series provides dual-axis measurement with 24-bit resolution and ±0.01° accuracy. Designed for compact robot joints, it measures both motor and joint output positions, simplifying design by replacing two encoders with one.
Outputs such as RS-485 and BiSS-C ensure seamless integration with modern robot controllers. This makes the T-Series ideal for cobots, dual-shaft systems, and applications where synchronized high-resolution feedback is essential.
By evaluating these factors, you can narrow down to the appropriate encoder model. The table below summarizes some of the key differences to help with selection:
| Application Scenario | Recommended Encoder | Rationale |
Single-Axis Feedback (Motor, Wheel) | S-Series | Thin Absolute Encoder, High Resolution, Simple Mounting |
| Dual-Axis Robot Joint | T-Series | Two Encoders in One Unit, Synchronized High-Precision Data |
Space-Constrained or Lightweight Design | S-Series (Compact) | Very Low Pprofile, Ideal for Gimbals, Servos, Small Robots |
| Extreme Precision Needs | T-Series | 24-bit Resolution, ±0.01° Accuracy for Demanding Tasks |
| High-Speed Rotation | S-Series | Rated for >20,000 RPM without Signal Loss |
| Harsh Industrial Conditions | S or T-Series | Sealed, EMI-Shielded, Immune to Contaminants |
Selecting the Right Encoder
1. Identify Sensing Needs – Single-axis feedback (motors, wheels) suits the S-Series; dual-axis systems (robot joints) benefit from the T-Series.
2. Resolution & Accuracy – For most control systems, 17-bit resolution from the S-Series suffices. Ultra-high precision (surgical robots, telescopes) calls for the T-Series.
3. Space & Form Factor – The slim S-Series fits into housings or gearboxes; the T-Series suits compact joints. Hollow shafts allow cable routing and flexible mounting.
4. Environmental Factors – Both series include EMI shielding and temperature ratings from –40 °C to 125 °C. The S-Series handles high speeds (>20,000 RPM), while the T-Series supports ~8,000 RPM for robotics.
5. Interfaces – Match output to your system: SSI, BiSS-C, RS-485, RS-422, or Tamagawa T485. Mosrac’s broad compatibility avoids costly converters.
6. Special Requirements – Multi-turn tracking, safety redundancy, or compact diameters are available within S-Series variants.
Application Examples
✔Robotic Joints & Cobots – The PT-Series integrates into compact joints, delivering accurate dual feedback while resisting vibration, ensuring safe, repeatable positioning.
✔Direct-Drive Motors & Machine Tools – S-Series encoders pair with torque motors in CNC systems for smooth, vibration-free motion, immune to thermal drift.
✔Medical Devices & Lab Automation – Compact, interference-resistant S-Series encoders provide reliable absolute feedback for surgical robots and lab automation without contamination risks.
✔Automotive & Aerospace – In steering modules, EV motors, or aerospace gimbals, encoders endure vibration, shock, and wide temperature swings while ensuring precision.
✔Industrial Motion Control – From printing rollers to solar trackers and conveyors, encoders deliver maintenance-free accuracy, even in dusty or outdoor environments.
In summary, encoders combine precision, resilience, and integration flexibility, offering engineers solutions tailored to robotics, motors, medical devices, and beyond.
With broad interfaces and robust designs, they reduce complexity while maximizing long-term system performance.
6. Market Trends, Future Outlook & Innovation
The global magnetic encoder market is experiencing steady growth, with market size valued at USD 3.25 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 5.93 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.83%. This rise reflects the growing demand for reliable, high-performance feedback devices in robotics, electric vehicles (EVs), and Industry 4.0 systems.
Unlike traditional optical encoders, magnetic solutions thrive in harsh environments, making them the preferred choice for modern automation.
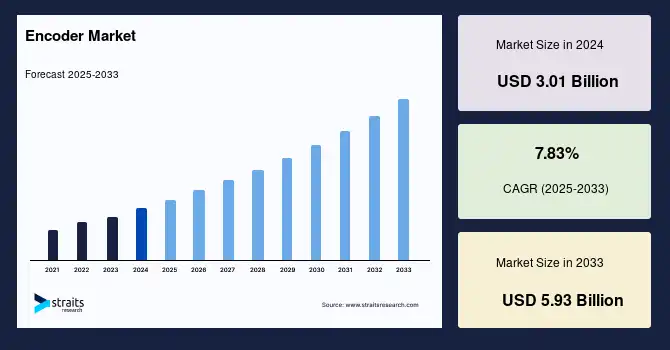
Encoder Market Size; Source: Straits Research
Robotics is a leading driver, as every joint and wheel in robots requires precise encoders. With manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare robots expanding globally, magnetic encoders offer the resilience and compactness needed.
The automotive sector is another catalyst, particularly EVs, where motors and drivetrains demand accurate, durable position feedback under heat and vibration. The demand is especially strong in the USA, China, Europe, and India, all of which are investing heavily in automation and electrification.
Looking ahead, innovation will shape the market further! Mosrac is advancing toward higher bit depths beyond 24-bit, on-board self-calibration, and even IoT-enabled diagnostics that predict failures before they occur. This aligns with Industry 4.0, where sensors not only control motion but also feed analytics systems for predictive maintenance.
Another frontier is AI-integrated automation. Future encoders may combine multi-modal sensing, such as torque or vibration data, giving AI richer input for smarter robots and assembly tools. Mosrac is also positioned to serve aerospace, micro-assembly, and semiconductor industries, where compact, resilient, and precise encoders are vital.
In summary, market trends point to robust growth, while Mosrac’s roadmap ensures innovation keeps pace with evolving automation needs, solidifying magnetic encoders as the feedback standard of the future.
7. Conclusion
High-performance automation relies on encoders that deliver precision, durability, and seamless integration. The magnetic encoders meet these demands, and they are proven to be the best in accuracy, resilience, and compact design.
With high resolutions, EMI resistance, and low-maintenance operation, they ensure reliable performance across robotics, motors, aerospace, and medical systems.
Their cost-effectiveness and long lifecycle provide manufacturers with lasting ROI and reduced downtime. With the advancement in automation, Mosrac continues to innovate and support clients with expert guidance.
Contact Mosrac today to explore solutions that will strengthen your systems and future-proof your automation investments!
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What are magnetic encoders?
A. Magnetic encoders use magnetic fields and Hall sensors to provide precise position feedback, offering durability and reliability in harsh industrial environments.
Q. What is the difference between incremental and absolute magnetic encoders?
A. Incremental magnetic encoders track relative motion with pulses, while absolute magnetic encoders provide a unique position value, ideal for robotics and direct-drive motor applications.
Q. Why choose Mosrac magnetic encoders over optical encoders?
A. Mosrac magnetic encoders outperform optical encoders with higher resilience, EMI shielding, and compact designs that deliver reliable feedback in dusty, oily, or vibrating environments.
Q. What is the advantage of using S-Series ultra-thin absolute encoders?
A. The S-Series magnetic encoder offers 17-bit resolution, ±0.05° accuracy, and a hollow, ultra-thin design, making it perfect for servo motors, robotic joints, and compact machinery.
Q. How do T-Series dual-axis magnetic encoders improve robotic joints?
A. T-Series dual-axis encoders provide 24-bit resolution and ±0.01° accuracy, enabling precise motor and joint position feedback in a single unit—ideal for cobots and automation robotics.
Q. Where are magnetic rotary encoders commonly used in industry?
A. Magnetic rotary encoders are widely used in robotics, EV motors, aerospace, CNC machines, and lab automation, delivering robust, high-resolution feedback for real-time control.